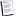 Dateline Carlsbad, CA
Dateline Carlsbad, CA
http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2013/01mar_twinpeaks/
March 1, 2013: Something unexpected is happening on the sun. 2013 is
supposed to be the year of Solar Max, the peak of the 11-year sunspot
cycle. Yet 2013 has arrived and solar activity is relatively low.
Sunspot numbers are well below their values in 2011, and strong solar
flares have been infrequent for many months.
The quiet has led some observers to wonder if forecasters missed the
mark. Solar physicist Dean Pesnell of the Goddard Space Flight Center
has a different explanation:
"This is solar maximum," he suggests. "But it looks different from what
we expected because it is double peaked."
Conventional wisdom holds that solar activity swings back and forth
like a simple pendulum. At one end of the cycle, there is a quiet time
with few sunspots and flares. At the other end, Solar Max brings high
sunspot numbers and solar storms. It’s a regular rhythm that repeats
every 11 years.
Reality, however, is more complicated. Astronomers have been counting
sunspots for centuries, and they have seen that the solar cycle is not
perfectly regular. For one thing, the back-and-forth swing in sunspot
counts can take anywhere from 10 to 13 years to complete; also, the
amplitude of the cycle varies. Some solar maxima are very weak, others
very strong.
Auroras Underfoot (signup)
Pesnell notes yet another complication: "The last two solar maxima,
around 1989 and 2001, had not one but two peaks." Solar activity went
up, dipped, then resumed, performing a mini-cycle that lasted about two
years.
The same thing could be happening now. Sunspot counts jumped in 2011,
dipped in 2012, and Pesnell expects them to rebound again in 2013: "I am
comfortable in saying that another peak will happen in 2013 and possibly
last into 2014," he predicts.
Another curiosity of the solar cycle is that the sun's hemispheres do
not always peak at the same time. In the current cycle, the south has
been lagging behind the north. The second peak, if it occurs, will
likely feature the southern hemisphere playing catch-up, with a surge in
activity south of the sun's equator.
Twin Peaks (shortfall, med)
Recent sunspot counts fall short of predictions. Credit: Dr. Tony
Philips & NOAA/SWPC [full plot]
Pesnell is a leading member of the NOAA/NASA Solar Cycle Prediction
Panel, a blue-ribbon group of solar physicists who assembled in 2006 and
2008 to forecast the next Solar Max. At the time, the sun was
experiencing its deepest minimum in nearly a hundred years. Sunspot
numbers were pegged near zero and x-ray flare activity flat-lined for
months at a time. Recognizing that deep minima are often followed by
weak maxima, and pulling together many other threads of predictive
evidence, the panel issued this statement:
"The Solar Cycle 24 Prediction Panel has reached a consensus. The panel
has decided that the next solar cycle (Cycle 24) will be below average
in intensity, with a maximum sunspot number of 90. Given the date of
solar minimum and the predicted maximum intensity, solar maximum is now
expected to occur in May 2013. Note, this is not a unanimous decision,
but a supermajority of the panel did agree."
Given the tepid state of solar activity in Feb. 2013, a maximum in May
now seems unlikely.
"We may be seeing what happens when you predict a single amplitude and
the Sun responds with a double peak," comments Pesnell.
Incidentally, Pesnell notes a similarity between Solar Cycle 24,
underway now, and Solar Cycle 14, which had a double-peak during the
first decade of the 20th century. If the two cycles are in fact twins,
“it would mean one peak in late 2013 and another in 2015.”
No one knows for sure what the sun will do next. It seems likely,
though, that the end of 2013 could be a lot livelier than the beginning.
|